Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan
For discussion of putting together a risk management plan, see Joe Taylor Jr.' S series, Risk Management. Once preliminaries are in place, the project manager can begin to put together the communication plan. A template for your communications plan is located in the media gallery. Ensure you cover the various scenarios including status updates. Risk Mitigation and Resilience. Heifer International empowers families and communities to plan for potential shocks through risk mitigation and to rebuild together through livestock and agricultural-based livelihoods to achieve resilience. Our approach is based on the sector concepts of absorption, adaptation and transformation. Virginia Hazard Mitigation Plan under the Disaster Mitigation Act of 2000, which is to qualify Northern Virginia’s localities for pre-disaster hazard mitigation project grants (should funds be made available) and for post-disaster hazard mitigation grants that would be in addition to the.
- Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan Example
- Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan Pdf
- Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan For Sale
Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan Example
I have to report risks and fill out the field 'mitigation'.
What does risk mitigation normally mean: reducing the likelyhood/probability or the impact?
3 Answers
In risk mitigation you look through your project looking for risks, their probability and their impact. After that create scenarios what you'll do in case the risk happens.
For example, you are doing construction in East Asia. The risk is the monsoon season starts earlier (it will definitely start, but the risk is that it starts earlier than you expect) and you'll do A and B in order to keep the project going and keep your employees safe.
Another example for IT. There is a risk that users are going to cancel their subscriptions to your service if you change a certain feature. As a mitigation, before launch you'll do an A/B test to see the if the risk is real, moreover you make it possible to turn the feature back on in case the number of users decreases more than you expect. Adobe creative cloud download.
You'll put all these into the document and ask other experts for review and insight.
ZsoltPrince 2 Post Mitigation Plan Pdf
ZsoltUnfortunately a lot of the time the concepts of 'risk mitigation' and 'risk response' are conflated.
There are several categories of risk response, of which mitigation is one. Specifically:
- Risk Avoidance. This is a response where you are reducing probability and/or impact to nil, usually by changing some aspect of the project like scope.
- Risk Transfer. Here you are handing responsibility for the risk to a third party. For example, if there is a liability risk you could transfer that risk by purchasing appropriate insurance.
- Risk Acceptance. This is basically a non-response, you have identified a risk but either you can't do anything about it or the impact of the risk is so minor that it isn't worth the effort to address it.
- Risk Mitigation. This response implies that you are reducing probability and/or impact of a risk, but the final probability/impact remain non-zero. These could be proactive approaches (e.g. we mitigate the risk that FDA won't approve our drug by seeking regular feedback from them on our licensure plan), or reactive (e.g. having a fallback plan in place in case the risk is realized).
- Risk Sharing. Here you are sharing the risk with a third party, for example a sub-contractor. Note that in this case you are also likely going to have to share some benefits.
Prince 2 Post Mitigation Plan For Sale
Using strict definitions, mitigation is what you do proactively to reduce either or both the probability and/or impact of a threat. After you perform the mitigation, you may end up with zero probability the threat will occur or have some residual risk remaining that is acceptable. A contingency plan is what you have in place after the threat occurs or when a certain trigger point occurs. So this is reactive.
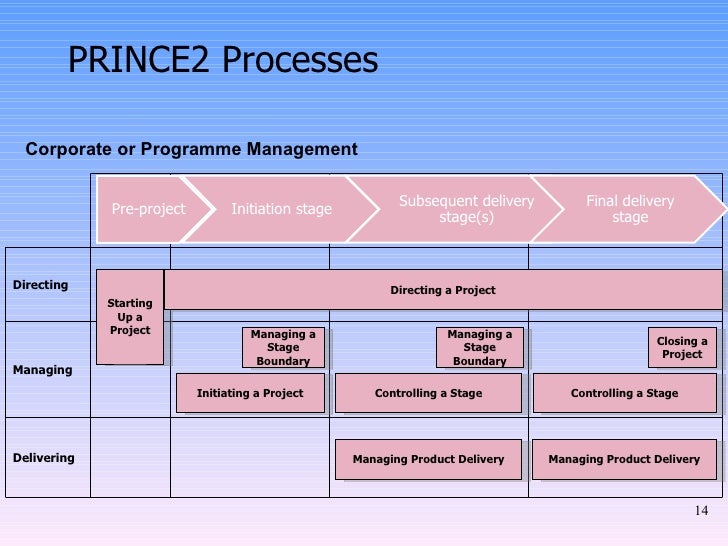
Here is where it becomes complex. We have a tendency to treat threats as discrete when in fact a threat is typically in a chain of threats. In other words, when on threat occurs, it becomes a risk factor of other threats to occur. Therefore, your contingency, or reactive plan, for the first threat is really a mitigation plan for the next set of threats. For example, when you start your car, you assume and accept some level of risk of a spontaneous tire failure. You mitigate this by rotating your tires at a set frequency, maintaining proper pressure, inspecting, etc. However, you still have some residual threat. If that threat occurs, you have a spare tire as your contingency plan. However, you now have other threats such as changing your tire next to the highway with the threat of getting hit, being stranded at night in the winter on a lonely, deserted road. And this continues on.
So I would recommend not getting bogged down with strict definitions. Risk management is about resilience. It is about looking at the entire chain of linked events and breaking the chain where you can or being able to continue if you can't break it by breaking another link down the line. Call it mitigation, contingency, recovery, plan B, avoidance, whatever.
EXCEPT, if you're studying for the PMP. Then learn the strict definitions.
David EspinaDavid Espina